Forced oscillations and resonance: EXP100030
This complete forced oscillations and resonance pack is designed to study, statically and dynamically, the simple spring pendulum.
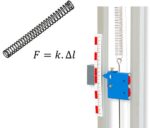
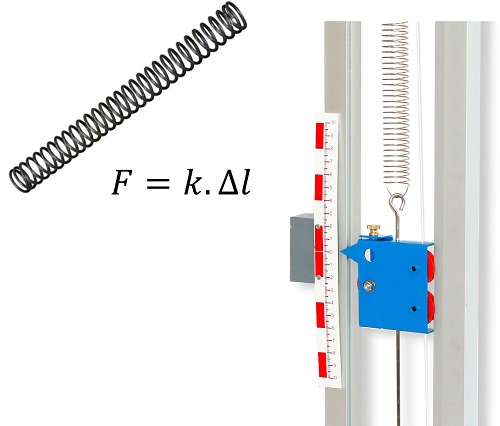
This complete forced oscillations and resonance pack is designed to study, statically and dynamically, the simple spring pendulum. A weight-holder platform is connected by a rod, and four weights are delivered with the device. A graduated rule, which can be moved to be placed in front of the mobile index linked to the spring, is used to read the elongations. A
test tube filled with water or oil is used to study fluid damping. Moreover, the weight-holder platform plunging into this test tube is interchangeable in the form of disks of various diameters, thus allowing variation of the friction coefficient. The
spring is coupled to a motor by a disk, thus ensuring sinusoidal excitation of the system. Excitation frequency is variable, while the static study is conducted simply with the motor shut down. Excitation frequency (adjustable from 0.1Hz to 3Hz) is displayed in digital figures on the motor box.
The apparatus is supplied with an accelerometer/ gyroscope for the acquisition.
STATIC STUDY: DETERMINING SPRING CONSTANT OF STIFFNESS
The aim is to determine the spring constant k of the available springs by measuring their elongation when balanced and loaded with masses of known weight: a spring is chosen and its unloaded length is measured. A mass is then placed at the end of this spring, and its new loaded length is measured. Repeat the operation with a number of masses to obtain the spring constant.
DAMPING STUDY
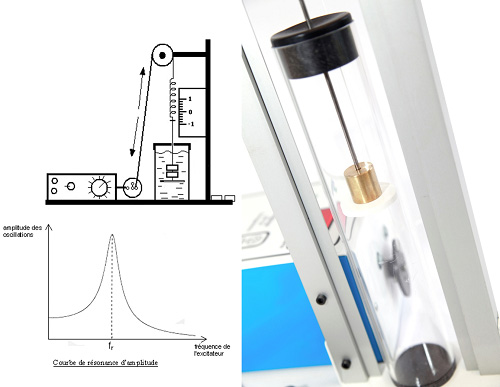
Fill the water cruet and, if necessary, adjust system height so that the mass remains in the water throughout the motion. Secure the mass with smallest diameter to the spring, and separate the mass vertically from its balanced position by 2 or 3 cm. Release the system and measure the system oscillation period. You can repeat the experiment with another mass or fluid.
RESONANCE STUDY
The oscillating system consists of the spring of least stiffness and of a small diameter cylindrical mass. Forced oscillations will be generated by motor rotation. Motor rotation speed and thus system oscillation frequency will be varied. Fill the graduated cruet with water and plunge the mass into it. Gradually adjust motor frequency to start system motion. Motor rotation frequency and spring oscillation frequency can thus be compared, and the resonance curve plotted.
SUBJECTS APPROACHED
»»Static and Hooke’s law
»»Free and forced oscillation dynamics
»»Fluid friction
»»System differential equation
»»System natural frequency
»»Damping rate
»»Resonance study
NECESSARY EQUIPMENT
| Reference | Description | quantity |
| PHD015130 | Oscillations study pack | 1 |
| DPM100010 | Accelerometer | 1 |
A computer is required
- Non catégorisé
- Electrical Engineering
- PHYSICS
- Energy & Systems
- Catalogues
- PDF catalogues